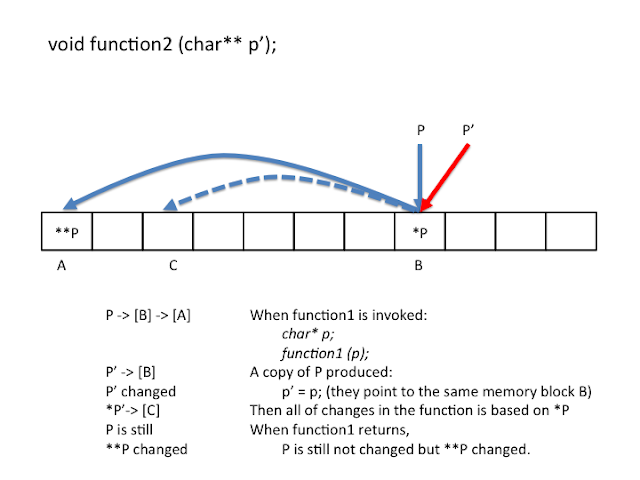
具体参见: http://landerchan.blogspot.com/2008/11/dynamically-allocating-multidimensional.html
Tuesday, 30 November 2010
Application of Double pointer in C
1. 作为参数, 用于函数改写指针参数。
2. 用来组建多维数组。
具体参见: http://landerchan.blogspot.com/2008/11/dynamically-allocating-multidimensional.html
具体参见: http://landerchan.blogspot.com/2008/11/dynamically-allocating-multidimensional.html
Tuesday, 23 November 2010
Linkage error for Linux package installation
Troubleshooting:cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
From MythTV
Jump to: navigation, search
This advice applies to those people running an SVN version of myth, not the tarball or packaged versions. If you see this:
/usr/local/bin/mythbackend: error while loading shared libraries: libmyth-0.20.so.0.20.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directoryafter updating myth, then you probably need to do the following:
sudo locate -u locate libmyth-0.20.so.0.20.0That will return something like
/home/mythtv/compile/svn/mythtv/libs/libmyth/libmyth-0.20.so.0.20.0 /usr/local/lib/libmyth-0.20.so.0.20.0The first one (for me) was the path to the folder I compiled MythTV in. The 2nd line is the installed location of libmyth. I need to add the folder its in (in this case /usr/local/lib/). You need to append that to the end of /etc/ld.so.conf. For me, I would now execute as root
echo "/usr/local/lib" >> /etc/ld.so.conf /sbin/ldconfigIf that doesn't work try make distclean, then configure, then make and make install.
If that all fails, try a fresh checkout of the svn repository, after deleting or moving your current checkout:
svn co http://svn.mythtv.org/svn/trunk/mythtv svn co http://svn.mythtv.org/svn/trunk/mythplugins svn co http://svn.mythtv.org/svn/trunk/myththemesThen go through the usual build process (configure && make && make install).
Reference: http://www.mythtv.org/wiki/Troubleshooting:cannot_open_shared_object_file:_No_such_file_or_directory
The meaning of printf(_("Some Strings"))
This is related international programming and GNU i18n. _() can be identified as the Macro of gettext() function. More details can be found here:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GNU_gettext
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GNU_gettext
Monday, 8 November 2010
Install wireshark on Fedora 11
1, yum install wireshark. this is quite straight forward.
2, yum install wireshark-gnome. This this necessary!!!
As for the installation on MAC OS X, this is still on working or I would rather give up. I don't want to make my MAC bulky.
2, yum install wireshark-gnome. This this necessary!!!
As for the installation on MAC OS X, this is still on working or I would rather give up. I don't want to make my MAC bulky.
Wednesday, 18 August 2010
Shell Script
When I was using Bash Shell script to extract the available free space in the hard driver, there are several things that are worth to be noticed.
1. The importance to declare variables.
There is a segment fault when I was trying to invoke the C program from the script if the arguments that are forwarded to the C program is not declared at the beginning of the script. Next step should be to make clear what is the meaning of the parameters when the declaration was made. Those are called "variable attributes" (Burth, 73)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Just found that the arguments can only be declared to be read-only......
If I did not use the declaration, there will be a segment fault. However, today I confirm that if I lost a argument of shell script such as the path of the experiment it will also lead to a segment fault!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I just found the main problem within this issue. The structure has problem:
df | while read content
do
echo ${content}
temp=${content}
done
echo ${content}
echo ${temp}
The situation is the same with the following snippet of code:
df | read content
echo ${content}
It can not read anything after "df".
1. The importance to declare variables.
There is a segment fault when I was trying to invoke the C program from the script if the arguments that are forwarded to the C program is not declared at the beginning of the script. Next step should be to make clear what is the meaning of the parameters when the declaration was made. Those are called "variable attributes" (Burth, 73)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Just found that the arguments can only be declared to be read-only......
If I did not use the declaration, there will be a segment fault. However, today I confirm that if I lost a argument of shell script such as the path of the experiment it will also lead to a segment fault!
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I just found the main problem within this issue. The structure has problem:
df | while read content
do
echo ${content}
temp=${content}
done
echo ${content}
echo ${temp}
The situation is the same with the following snippet of code:
df | read content
echo ${content}
It can not read anything after "df".
Tuesday, 10 August 2010
C++ Programming Tips...
Converting from a String to a integer can be achieved by a build-in function atoi() which can be found from the manual page. However the conversion from a integer to a String can not follow the similar method due to the itoa() function is not a build-in function. It is a compiler dependent method. In C++, there is a handy method:
#include
int number;
std::ostringstream sin;
sin << number;
std::string aString= sin.str();
char* c_type_string = aString.c_str();
#include
int number;
std::ostringstream sin;
sin << number;
std::string aString= sin.str();
char* c_type_string = aString.c_str();
Friday, 16 July 2010
Agenda For the Meeting on 16th, July and Tasks to complete
I am a little behind the progress. At this time, what I should consider is what I have found from the graphs or the charts and how to defineto explain them, instead of what I know about a specific system.
There are mainly two parts of the tasks to complete:
1. (To be complete by next Wednesday or Thursday) The results and clear descriptions of the Experiment of Chord.
2. (To be complete by 11th of Aug, when Nick is coming back)
- Technical differences between Kademlia and Coral:
Why Coral is used in small files sharing?
Why Kademlia is used in big files sharing?
- Two methods to prove what I will find:
Literatures of both these two methods
Experiments on both these two methods?
Experiments on a range of file sizes to compare the differences between these two methods.
- How to define and then to measure the closeness?
- How effectively the location of peers affect the performance of the system?
When we talking about the Experiments, there are something should be concerned:
- Closeness number of hops
- Latency - routing latency
- file transfer latency (bandwidth, hidden conjunction problems two users who request resources are allocated into two different download networks with two different environments, one is conjuncted and one is not that busy)
- Distances (Real-distance/Political distance and topological distance) Is there relation between these distance and two previous notations? Find it out!!
- Load on each nodes (download loads, upload loads, forwarding loads and so on.)
- Routing table information stored in each node.
- Capability of each node and how to measure each node's system consumption for a system's running.
- Mobility, the distribution issue in a mesh network constructed with mobiles. Mobiles are movable and how to distribute the news to each of them is the central issue. For example, Madonna's new songs are released and how to forward these songs to each of her fans.
There are mainly two parts of the tasks to complete:
1. (To be complete by next Wednesday or Thursday) The results and clear descriptions of the Experiment of Chord.
2. (To be complete by 11th of Aug, when Nick is coming back)
- Technical differences between Kademlia and Coral:
Why Coral is used in small files sharing?
Why Kademlia is used in big files sharing?
- Two methods to prove what I will find:
Literatures of both these two methods
Experiments on both these two methods?
Experiments on a range of file sizes to compare the differences between these two methods.
- How to define and then to measure the closeness?
- How effectively the location of peers affect the performance of the system?
When we talking about the Experiments, there are something should be concerned:
- Closeness number of hops
- Latency - routing latency
- file transfer latency (bandwidth, hidden conjunction problems two users who request resources are allocated into two different download networks with two different environments, one is conjuncted and one is not that busy)
- Distances (Real-distance/Political distance and topological distance) Is there relation between these distance and two previous notations? Find it out!!
- Load on each nodes (download loads, upload loads, forwarding loads and so on.)
- Routing table information stored in each node.
- Capability of each node and how to measure each node's system consumption for a system's running.
-
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)